
CHECK NETWORK MAC ADDRESS HOW TO
How to Find an IP Address Using a Mac Address? Now that we know what IP and MAC addresses and the underlying ARP are let’s see how you can find an IP address using a MAC address. This is also done to prevent cyber attackers from stealing IP and MAC addresses by accessing the ARP cache.
CHECK NETWORK MAC ADDRESS FREE
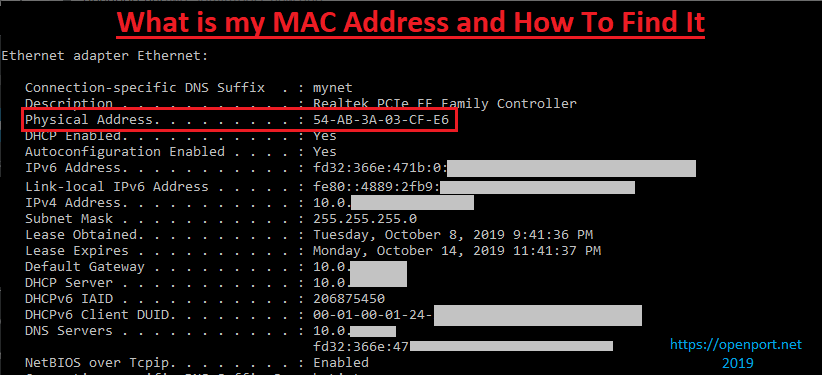
This is by design, and it is purged regularly to free the space. The size of the ARP cache is limited, so addresses stay on for a specific time only. Otherwise, it sends a new request for the mapping. The ARP system has something called an ARP cache or a table that maps a system’s IP and MAC address, and it immediately looks up this table to give the pertinent information.Įvery time a device sends a message, the gateway ensures that the IP-MAC address is mapped. This gateway turns to the ARP system for getting the associated MAC address. A piece of hardware equipment called the gateway is responsible for allowing these packets to and from a device. This computer starts communicating with other computers by sending and receiving data packets. So, how does ARP help? Working of the ARPĮach time a new computer is added to the network, it gets a unique IP address. As you know, IPv4 uses 32 bits, but MAC uses 48 bits, and a protocol like ARP bridges the difference between these two lengths. It is impossible to map the IP address with the MAC directly because they have different formats and lengths, so an intermediary mapping protocol becomes essential. What is ARP?ĪRP is a set of procedures that connect an IP address that could change depending on the device’s location to the fixed MAC address hardwired into each NIC. Note that MAC addresses are fixed while IP addresses keep changing. Using the Address Resolution Protocol (ARP), you can use this MAC address to identify a device’s IP using the Address Resolution Protocol (ARP). As you may have guessed, this is also a unique identifier used for communications within a network. Media Access Control (MAC) address is a six-byte or 12-digit hexadecimal number hardcoded to a Network Interface Controller or Card. But before that, let’s understand what a MAC address is. What is a MAC Address?įinding a device’s IP address using the MAC address is a relatively lengthy process. Otherwise, you’ll have to look for other information like a MAC address through which you can identify the IP address.Īnd that’s precisely what we’re going to see next. What happens if you must know the IP address of another device? If you know the associated URL like, you can use it. Scroll down to see your IPv4 and IPv6 addresses. To find the IP address of your device, go to Command Prompt, and type “ ipconfig“. How to Find the IP Address of Your Device? Now that you know what an IP address is, let’s see how you can find it. This format is called the IPv4, and since the sheer number of websites have exhausted all possible options that come with IPv4, the world is slowly migrating to IPv6, which contains 128 bits compared to the 32 bits IPv4. As you can see, IPv4 uses 32 bits to identify a device uniquely.
.png)
Each of these can be a number from 0 to 255.įor example, the IP address of the Google server is 8.8.8.8 while that of ESPN is 45.63.254.129. This machine-readable address is the IP address, and it is in the form of. This entire process is quicker than the battling of your eyelid, and that’s why we don’t know its complexity. Finally, a message is sent to that server, and the contents received from it are displayed on your browser. Next, these numbers are used to identify the location and the server that contains the information we need. Whenever you open a website, your browser sends a request to the Domain Naming Server, where the human-readable URL is converted into a machine-readable set of numbers. Internet Protocol (IP) address is a set of numbers that play a two-pronged role in a network – one to identify a device uniquely and the other to identify its location. This unique address is called the IP address. In other words, every device on a network has a unique address that helps with its identification. Just like how individuals are unique, devices are unique too! Not in a physical sense but by the way they identify themselves in a network.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
